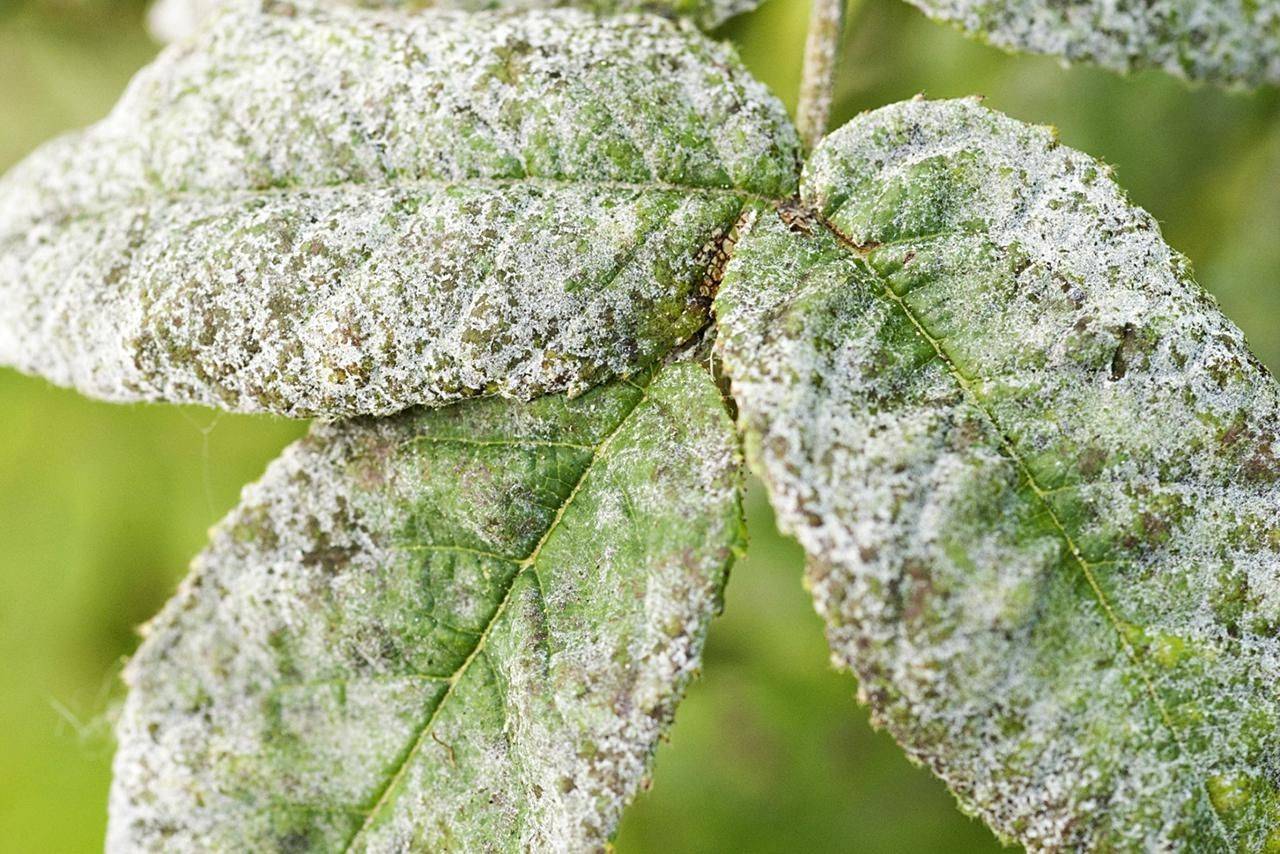
Powdery mildew is a widespread fungal disease that affects numerous plant species, leading to reduced yields and aesthetic damage.
This article reviews the preventive measures and treatment options available for managing powdery mildew, focusing on cultural practices, chemical control, and biological approaches.
1. Introduction:
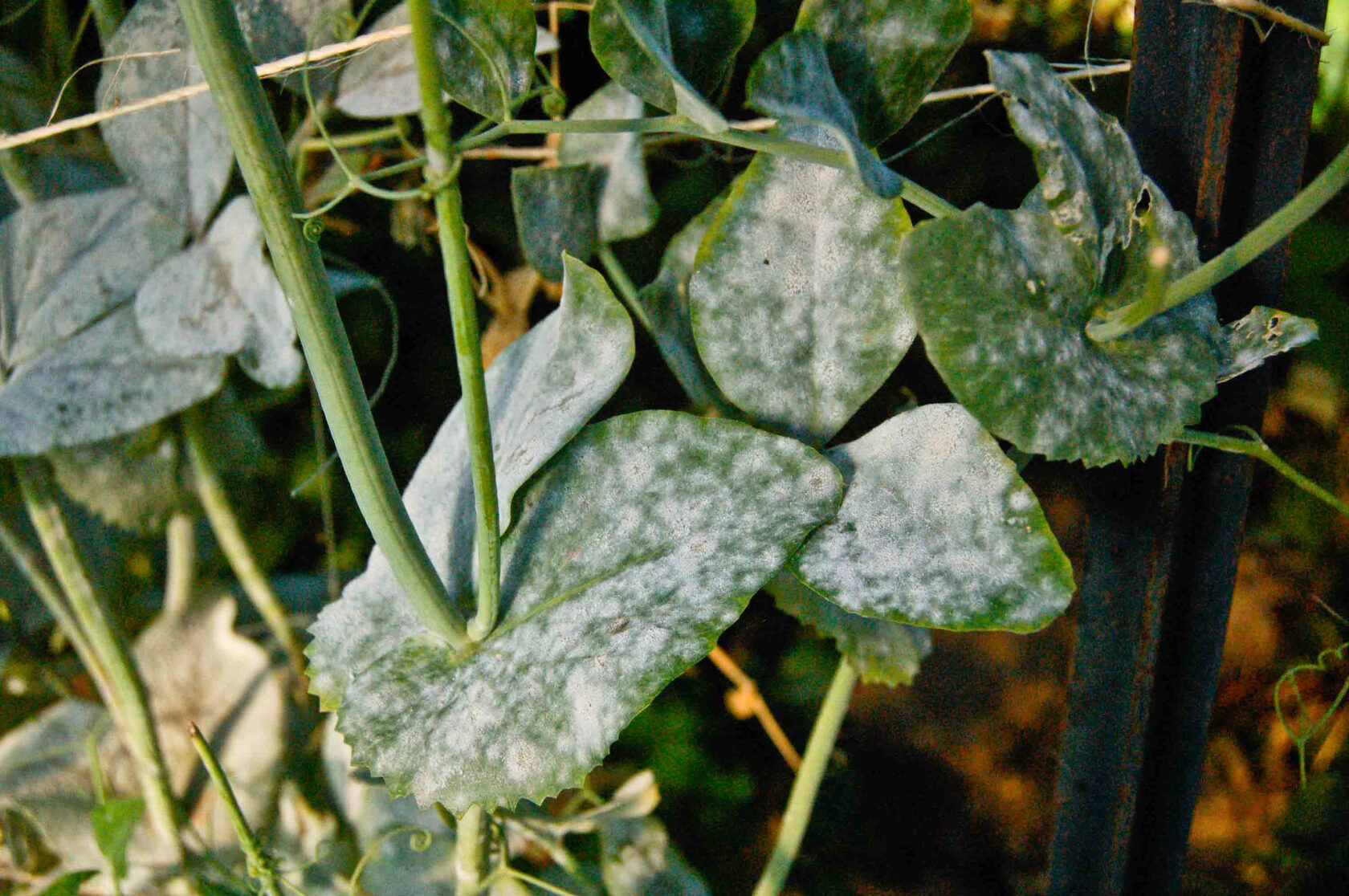

2. Cultural Practices for Prevention:
- Plant selection: Choose resistant or tolerant cultivars when available, as they exhibit reduced susceptibility to powdery mildew.
- Proper spacing: Ensure adequate plant spacing to promote air circulation and reduce humidity around the plants, creating an unfavorable environment for fungal growth.
- Pruning: Remove infected plant parts promptly, especially during the dormant season, to minimize overwintering of the fungus.
- Irrigation management: Avoid overhead watering and opt for drip irrigation or other methods that keep foliage dry, as wet conditions facilitate powdery mildew development.
- Sunlight exposure: Select planting sites with proper sunlight exposure, as direct sunlight helps reduce humidity and inhibits fungal growth.
3. Chemical Control:
- Fungicides: Apply specific fungicides labeled for powdery mildew control according to recommended timings and rates. Contact fungicides, such as sulfur or horticultural oils, are effective against powdery mildew and should be used preventively or at the first signs of infection.
- Systemic fungicides: Systemic products that penetrate plant tissues, such as triazoles or strobilurins, can provide long-lasting protection against powdery mildew. Rotate fungicides with different modes of action to minimize the risk of resistance development.
- Application techniques: Proper and thorough coverage is crucial when using fungicides, especially on the lower leaf surfaces, where powdery mildew often initiates.
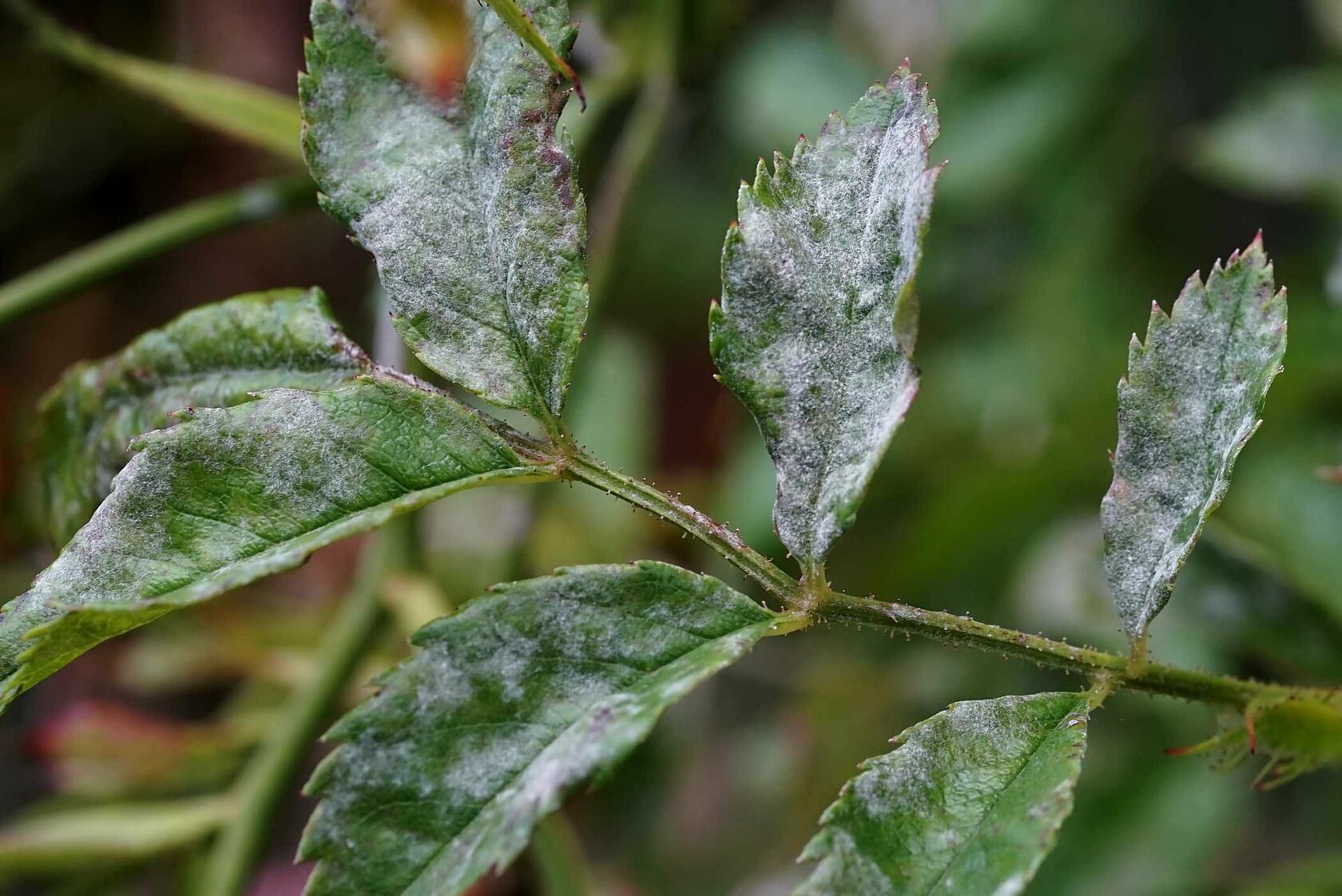

4. Biological Control:
- Biofungicides: Utilize microbial-based products, such as Bacillus subtilis or Ampelomyces quisqualis, which compete with the fungus and reduce the severity of powdery mildew infections.
- Beneficial insects: Encourage the presence of natural enemies, such as ladybugs or lacewings, which feed on powdery mildew spores and help control its spread.
5. Integrated Pest Management (IPM):
Adopting an integrated approach is the most sustainable and effective method for managing powdery mildew. This involves combining cultural practices, chemical control, and biological agents while monitoring disease development. Integrated pest management also emphasizes the use of resistant cultivars and regular scouting to detect early signs of infection.
Conclusion: